Chronic ITP can be a serious condition and should be managed properly
What is ITP?
ITP is short for immune thrombocytopenia (THROM-bo-sigh-toe-PEE-nee-uh).
ITP is an autoimmune disorder, which means that the body’s immune system attacks and destroys platelets in the blood. ITP can also slow down the body’s ability to make more platelets.
What is chronic ITP?
ITP can become chronic, which is when platelet counts are low for a long time. Chronic ITP can be a serious condition if left untreated. It’s important to know that chronic ITP can be managed with treatment.
You may need to see a new healthcare provider who specializes in treating blood disorders, like a hematologist-oncologist (called a “hem-onc” for short).
Keep in mind that ITP is not cancer and it is not contagious.
What are platelets?
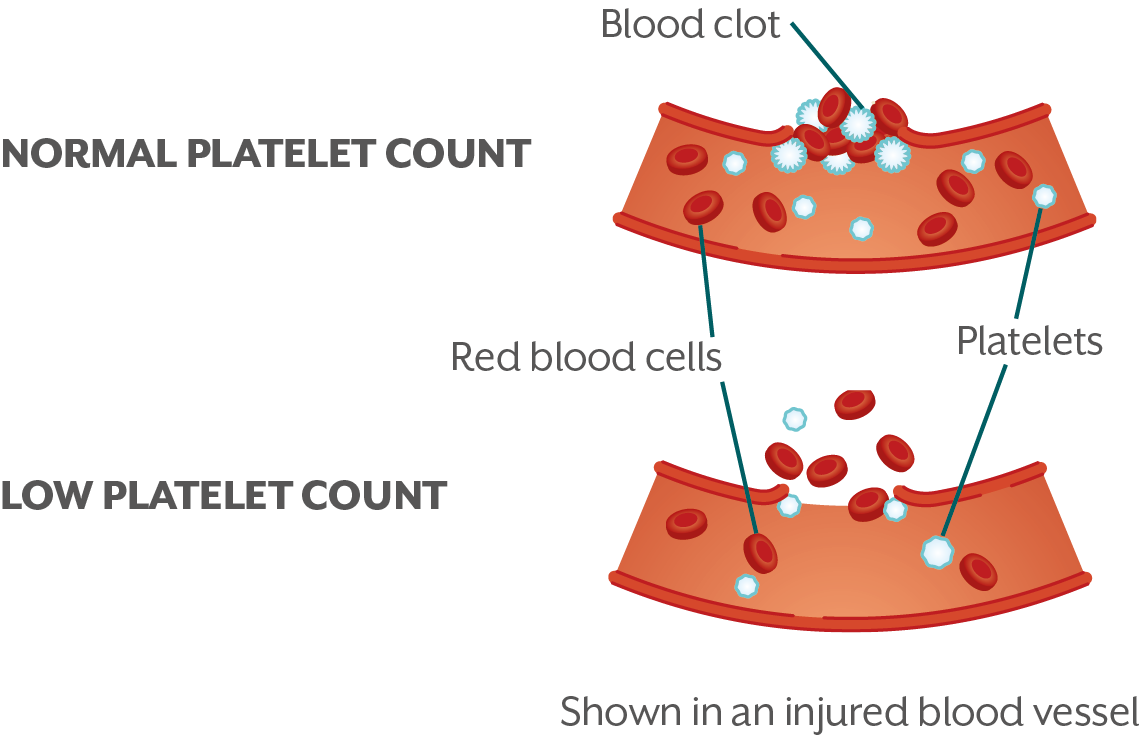
Platelets are tiny cells in the blood that clump together to form a clot and stop the bleeding when a blood vessel is damaged. For example, when your body forms a scab, or clot, over an injury, platelets are the first cells on the scene to begin the healing process. People with ITP have lower amounts of platelets in their blood, which makes it harder for clots to form.
What happens when you have low platelet counts?
Low platelet counts can lead to bleeding and other issues. Every person’s body is different, so your symptoms may vary. Your symptoms may include:

- Tiny reddish-purple spots called petechiae (puh-TEE-kee-uh)
- Easy bruising

- Bleeding from gums or nose
- Bruising or blood-red spots in the mouth

- Very heavy or long menstrual flow
- Internal bleeding (for example, in the stomach, intestines, or brain)
Treatment is individualized
What is the goal of treatment?
The goal of treatment in ITP is to reduce the risk of bleeding by raising platelet counts. The target number of platelets needed will vary from person to person. You and your healthcare practitioner will determine the right treatment for you to achieve that goal.
Many people set goals for themselves based on their lifestyle and daily activities. Write down your own goals and other personal priorities. Share them with your healthcare provider when discussing your treatment options.
What is the right platelet count for me?
Every person is different. You and your healthcare provider will determine what the right platelet target is for you.
Healthcare providers usually consider treatment when someone with ITP has:
- Platelet counts below 20,000 per microliter (μL)
- Bleeding symptoms
TAVA_ITP-22133 0822


